Acne is a prevalent skin condition that affects people of all ages, races, and ethnicities, including the population in Kenya. It is characterized by the appearance of blemishes such as pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and nodules on the skin’s surface. Acne can be a source of physical discomfort and emotional distress, impacting one’s self-esteem and confidence. Understanding the different types of acne prevalent in Kenya and their underlying causes is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Different Types of Acne Prevalent in Kenya
1. Comedonal Acne
Comedonal acne is a common form of acne that primarily involves the presence of blackheads and whiteheads. These blemishes occur when the hair follicles become clogged with dead skin cells, oil (sebum), and other debris. Blackheads are open comedones that appear black due to oxidation, while whiteheads are closed comedones that have a white or flesh-coloured appearance. Comedonal acne is commonly seen on the forehead, nose, and chin areas.
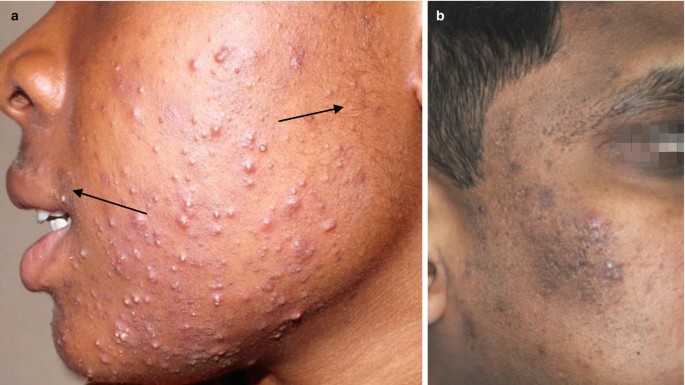
Causes: Comedonal acne is often triggered by excessive sebum production, hormonal fluctuations, certain skincare products, and environmental factors. In Kenya, climate and humidity can contribute to increased oil production, making individuals more susceptible to this type of acne.
Management: To manage comedonal acne, gentle exfoliation with salicylic acid or alpha hydroxy acids can help unclog the pores and remove dead skin cells. It’s essential to use non-comedogenic skincare products that do not block the pores, and avoid overwashing or scrubbing the affected areas, as this can irritate the skin and exacerbate the condition.
2. Papules and Pustules
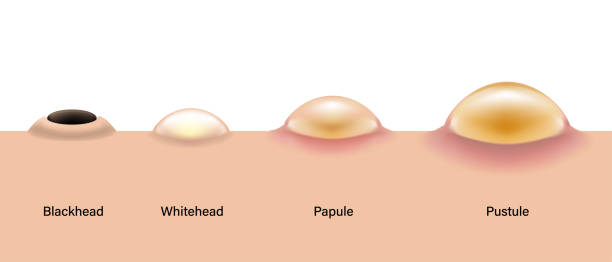
Papules and pustules are the more commonly recognized forms of acne, and they often appear as red, inflamed bumps on the skin’s surface.
Papules are small, solid, and tender lesions that do not contain any visible pus. They result from the inflammation of blocked hair follicles and are caused by the immune system responding to bacteria trapped within the follicles.
Pustules, on the other hand, are similar to papules but have a white or yellow center, indicating the presence of pus. They occur when the body’s immune response sends white blood cells to combat the bacterial infection. Hence, resulting to the formation of pus.
Causes: Papules and pustules can arise from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, stress, diet, and genetics. Additionally, certain makeup products and skincare items containing pore-clogging ingredients may exacerbate this type of acne.
Management: Avoid picking or squeezing papules and pustules, as this can lead to scarring and spread the infection to adjacent areas. Topical treatments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can be effective in reducing inflammation and controlling bacterial growth.
3. Nodular and Cystic Acne
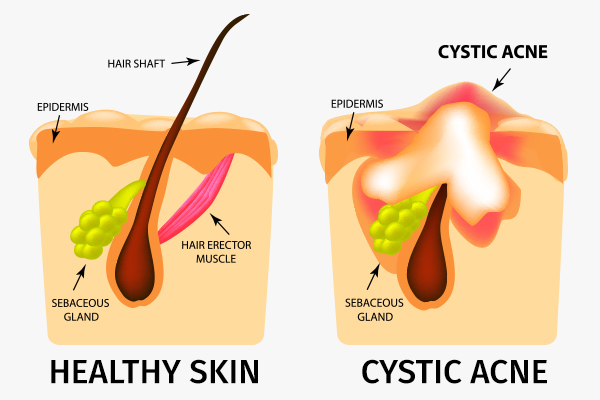
Nodular and cystic acne are severe forms of acne that occur beneath the skin’s surface and are often painful. They are characterized by large, deep, and inflamed lesions.
Nodules are hard, solid lumps formed by the buildup of bacteria, sebum, and dead skin cells deep within the hair follicles. They are often more substantial and more painful than papules or pustules.
Cysts are pus-filled, fluid-filled, or semi-solid sacs that form deep within the skin. They are often larger than nodules and can lead to significant scarring if not treated properly.
Causes: Nodular and cystic acne can result from an overgrowth of acne-causing bacteria, increased sebum production, hormonal imbalances, and sometimes even certain medications. In Kenya, genetics, diet, and lifestyle factors can play a role in the development of severe acne.
Management: Given the severity of nodular and cystic acne, it is essential to seek professional help from a dermatologist. Prescription medications, such as oral antibiotics, hormonal treatments, or isotretinoin (a potent medication derived from Vitamin A), may be prescribed to control the condition. Dermatologists may also perform intralesional corticosteroid injections or drainage procedures to reduce inflammation and prevent scarring.
4. Acne Conglobata:
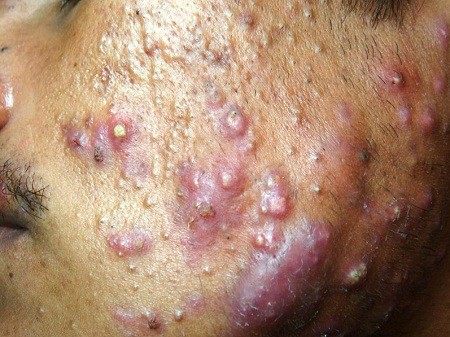
Acne conglobata is an uncommon and severe type of acne that goes beyond traditional nodular and cystic acne. It is characterized by interconnected nodules and abscesses, leading to significant inflammation and tissue damage.
Causes: The exact cause of acne conglobata is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, and a hyperactive immune response to bacteria. In some cases, anabolic steroid use may also contribute to the development of this condition.
Management: Acne conglobata necessitates immediate medical attention and treatment. Dermatologists may prescribe a combination of oral antibiotics, retinoids, and hormonal medications to address the underlying causes. In some cases, surgical drainage or excision of large abscesses may be required to prevent further complications and scarring.
5. Acne Mechanica:
Acne mechanica is a type of acne caused by mechanical factors, such as friction, pressure, or heat on the skin. It is common among athletes or individuals who frequently wear tight-fitting clothing or use equipment that rubs against the skin, like helmets or straps.
Causes: In Kenya, climate conditions, especially during hot and humid seasons, can exacerbate acne mechanica due to increased sweating and skin occlusion. Sports activities and the use of certain equipment can also contribute to the development of this type of acne.
Management: Prevention is crucial for managing acne mechanica. This involves wearing loose, breathable fabrics, changing out of sweaty clothing promptly, and using non-comedogenic skincare products to minimize pore blockages. Additionally, applying a barrier cream or gel to potential problem areas before engaging in sports or other activities can reduce friction and irritation.
6. Acne Fulminans
Acne fulminans is an extremely rare and severe type of acne that can manifest abruptly and dramatically. It is characterized by the sudden onset of painful and ulcerating acne lesions. Which is accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, joint pain, and malaise.
Causes: The exact cause of acne fulminans is not fully understood. It is believed to be related to an abnormal immune response, hormonal imbalances, or even underlying infections.
Management: Acne fulminans requires immediate medical attention, and individuals experiencing this condition should seek emergency medical care. Treatment often involves oral steroids, immunosuppressive drugs, and antibiotics to control the inflammation and infection. Dermatologists may also recommend wound care and therapies to address scarring and promote healing.
Conclusion:
Acne is a prevalent skin condition that can significantly impact an individual’s physical and emotional well-being. In Kenya, factors such as climate, genetics, and lifestyle can contribute to the development of different types of acne. Understanding the various types of acne and their causes is essential for effective management and prevention.
Mild forms of acne can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments and proper skincare routines. While more severe cases require professional intervention from a dermatologist. Early and appropriate treatment can help minimize the risk of scarring and long-term skin damage.
In addition to seeking professional help, adopting a consistent skincare routine, avoiding pore-clogging products, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to clearer and healthier skin. Remember that each individual’s skin is unique. Therefore, finding the most suitable approach to managing acne might require some trial and error. Prioritize gentle care, and always consult a skin care specialist when needed to achieve optimal results in managing and preventing acne.

